Figure by Jenny Douthett and Ted Eckmann
|
|
Wind is made of air that is in motion relative to the Earth's surface. Wind speed is the ratio of a unit distance covered by the air to the time taken to cover it. Winds are typically named for the direction from which the wind is blowing (so a wind coming from the west would be a "westerly" wind, and a sea breeze would be wind blowing from the sea towards the land). Exceptions to this rule include "onshore" breezes, which are winds blowing onto the shore (from the water) and "offshore" breezes, which are blowing from the shore towards the water.
 Figure by Jenny Douthett and Ted Eckmann |
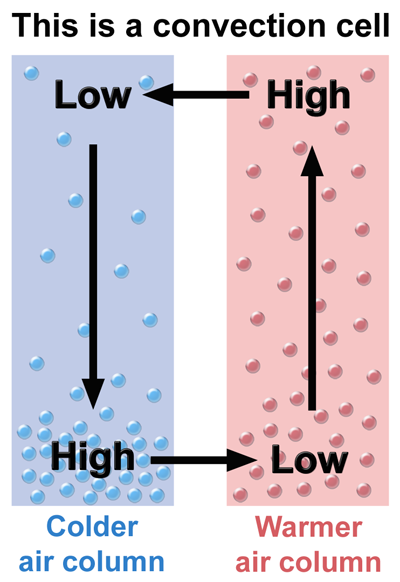
Air pressure is basically the weight of all the air on top of a point in the atmosphere. Winds are created primarily by pressure gradients, which arise when air pressure changes with geographical location. These pressure gradients are created primarily by having different air temperatures in different areas. In the diagram above, those are areas of “high” air pressure compared to other areas at the same altitude, and areas of “low” air pressure compared to other areas at the same altitude. These create horizontal pressure gradients that point from “highs” to “lows.” Winds usually only blow from high to low pressure in the horizontal.
High and low pressures are relative: the warm column has a higher pressure at its top than the cold column does at its top. The cold column has a higher pressure at its bottom than the warm column does at its bottom. Vertical pressure gradients are huge (from 1000 mb to 500 mb in ~5700 m) compared to horizontal: the highest and lowest sea-level pressures ever recorded are within 300 mb of each other. Air pressure always decreases with altitude. But the downward force of gravity almost exactly cancels out these upward pressure gradients, leaving the atmosphere in “hydrostatic balance.” Thus, vertical winds are usually very weak and slow.
We measure winds using the R. M. Young Wind Monitor, Marine grade This photo shows us setting up the wind sensor. Photo by Meri Marsh; May 25, 2007 Click here for a larger version of the photo |
 |
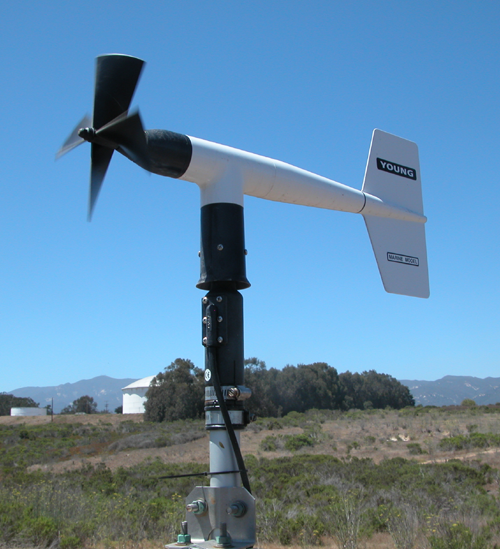 |
Anemometer at Coal Oil Point Reserve. |
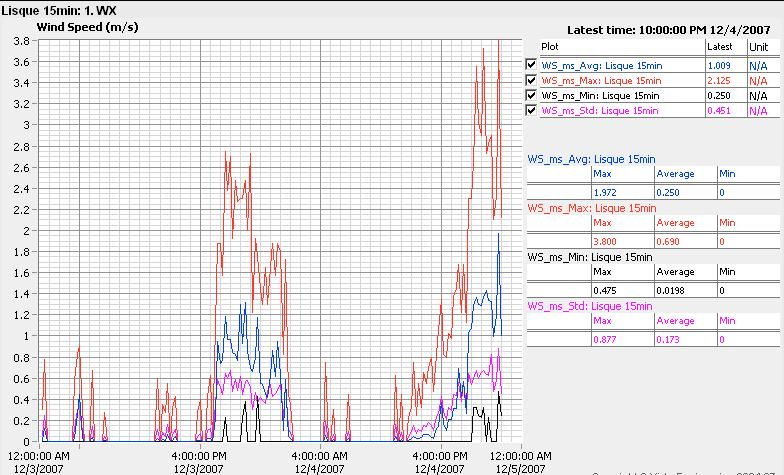
EXAMPLE DATA
Click here to see animations showing spatial and temporal patterns in winds. |